Can stress cause low oxygen levels? Stress has a profound impact on the body, and one area it can affect is your oxygen levels. When you’re stressed, your breathing patterns and respiratory function can change, leading to a drop in oxygen saturation. This article explores how stress influences your oxygen levels and provides ways to manage these effects.
Key Takeaways
- Chronic stress can constrict airways and reduce oxygen levels, particularly in individuals with existing respiratory conditions.
- Breathing techniques like belly breathing and pursed lip breathing can effectively manage stress-induced breathing difficulties and improve oxygen intake.
- Monitoring oxygen saturation is critical for managing respiratory health during stress, with levels below 95% indicating potential hypoxemia needing intervention.
The Physiological Impact of Stress on the Body
Stress triggers a complex array of physiological responses aimed at preparing the body for a “fight or flight” situation. When faced with stress, your body releases hormones that increase blood flow to muscles and vital organs, effectively enhancing oxygen delivery during emergencies. Your heart rate and blood pressure also rise, ensuring that your body can respond quickly to threats. While these responses are beneficial in short bursts, chronic stress can take a toll on your body.
One of the most significant impacts of stress is its effect on your respiratory system. During stressful situations, you may experience rapid breathing as your body attempts to meet increased oxygen demands. However, stress can also constrict your airways, leading to reduced oxygen levels in your blood. This constriction can make it harder for your body to function properly, especially if you already have underlying conditions such as asthma or COPD.
The physiological responses triggered by stress are not just limited to immediate effects. Over time, chronic stress can contribute to more severe health issues, including heart disease and heart failure. The increased strain on your heart and blood vessels can lead to an increased risk of heart attack and other symptoms. If you experience symptoms of chronic stress, it is important to address them promptly.
Understanding these connections underscores the importance of managing stress factors to determine overall health and well-being and to ensure that good things happen.
How Stress Affects Breathing Patterns
When stress takes hold, it often changes the way we breathe. Many people under stress exhibit shallow breathing patterns that primarily engage the upper chest. This type of breathing is inefficient and can lead to an imbalance of gases in the body. Instead of taking deep breaths that fully utilize the lungs, stressed individuals often take quick, shallow breaths that do not provide enough oxygen.
Chronic stress can further exacerbate existing respiratory conditions, making breathing more difficult. For individuals with conditions like asthma or COPD, the added strain of stress can lead to increased episodes of breathlessness and other symptoms. The feeling of not being able to breathe properly can itself become a source of anxiety, creating a vicious cycle that is hard to break.
Fortunately, there are effective breathing exercises that can help manage stress-induced breathing difficulties. Techniques like pursed lip breathing and belly breathing can help control breathing pace, allowing for more effective air exchange and easing shortness of breath. These exercises not only improve oxygen intake but also promote relaxation, making it easier to cope with stress.
The Link Between Chronic Stress and Oxygen Saturation Levels
Chronic stress doesn’t just affect how you breathe; it can also lead to decreased oxygen levels in your body. When stress becomes a constant presence in your life, it can exacerbate symptoms for individuals with conditions like COPD, further worsening overall respiratory function.
Oxygen saturation levels, which measure the amount of oxygen circulating in your blood, can fall below healthy levels due to chronic stress. Hypoxemia, characterized by blood oxygen levels below 95%, can occur as a result of low blood oxygen levels. This condition can lead to serious health complications, including confusion, shortness of breath, and even life-threatening situations if not addressed promptly.
It’s crucial to recognize the symptoms of low oxygen levels, which can include lightheadedness, a feeling of breathlessness, and confusion. By understanding the link between chronic stress and oxygen saturation, you can take proactive steps to manage stress and maintain healthy oxygen levels.
The Role of Anxiety in Low Oxygen Levels
Anxiety often goes hand in hand with stress, and it plays a significant role in affecting oxygen levels in the body. When anxiety levels rise, the body uses more oxygen due to the increased metabolic rate. This can lead to a higher oxygen demand that the body may struggle to meet.
During a panic attack, hyperventilation is a common response. This rapid breathing disrupts the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide, leading to inadequate oxygen exchange and lower O2 saturation. The result is a sensation of breathlessness and further anxiety, which can exacerbate the problem. Panic attacks can intensify these feelings.
Individuals with anxiety and depression often experience more respiratory symptoms, such as breathlessness. This is why it’s essential to address mental health issues as part of a comprehensive approach to improving respiratory health and maintaining healthy oxygen levels.
Monitoring Oxygen Levels During Stress
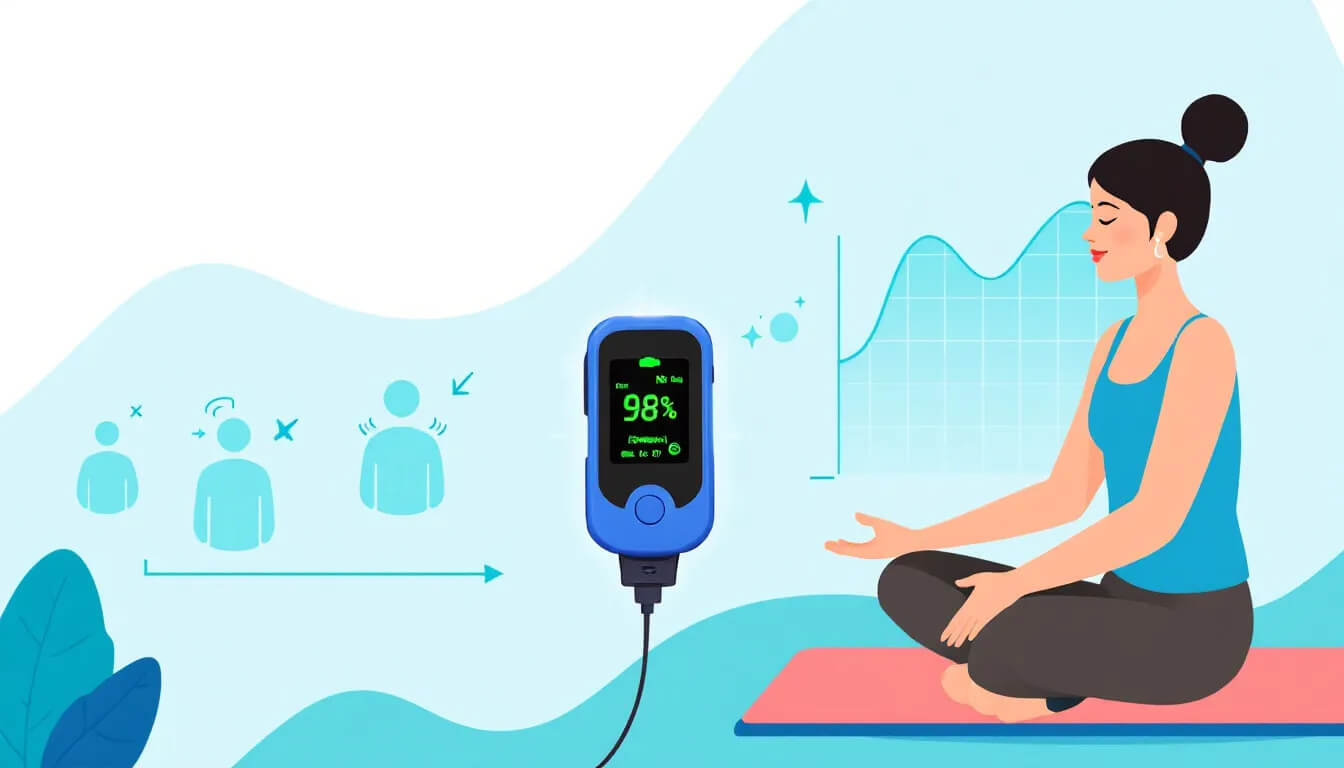
Monitoring your oxygen levels is a critical step in managing the impact of stress on your respiratory health. Common methods to assess oxygen levels include a Physical Exam, a pulse oximeter, and arterial blood gas (ABG) tests. Pulse oximetry is a fast and non-invasive way to measure oxygen saturation levels, with a small device attached to your fingertip.
For more precise measurements, an ABG test can be conducted to analyze the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood. These tests are particularly important for patients with acute respiratory issues, as they help healthcare providers monitor oxygen levels and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
Understanding your oxygen saturation levels is crucial. An oxygen saturation level over 95% is considered healthy, while levels below this threshold can indicate hypoxemia. Regularly monitoring your oxygen levels allows for timely action to address issues and maintain optimal respiratory health.
Managing Stress to Improve Oxygen Levels
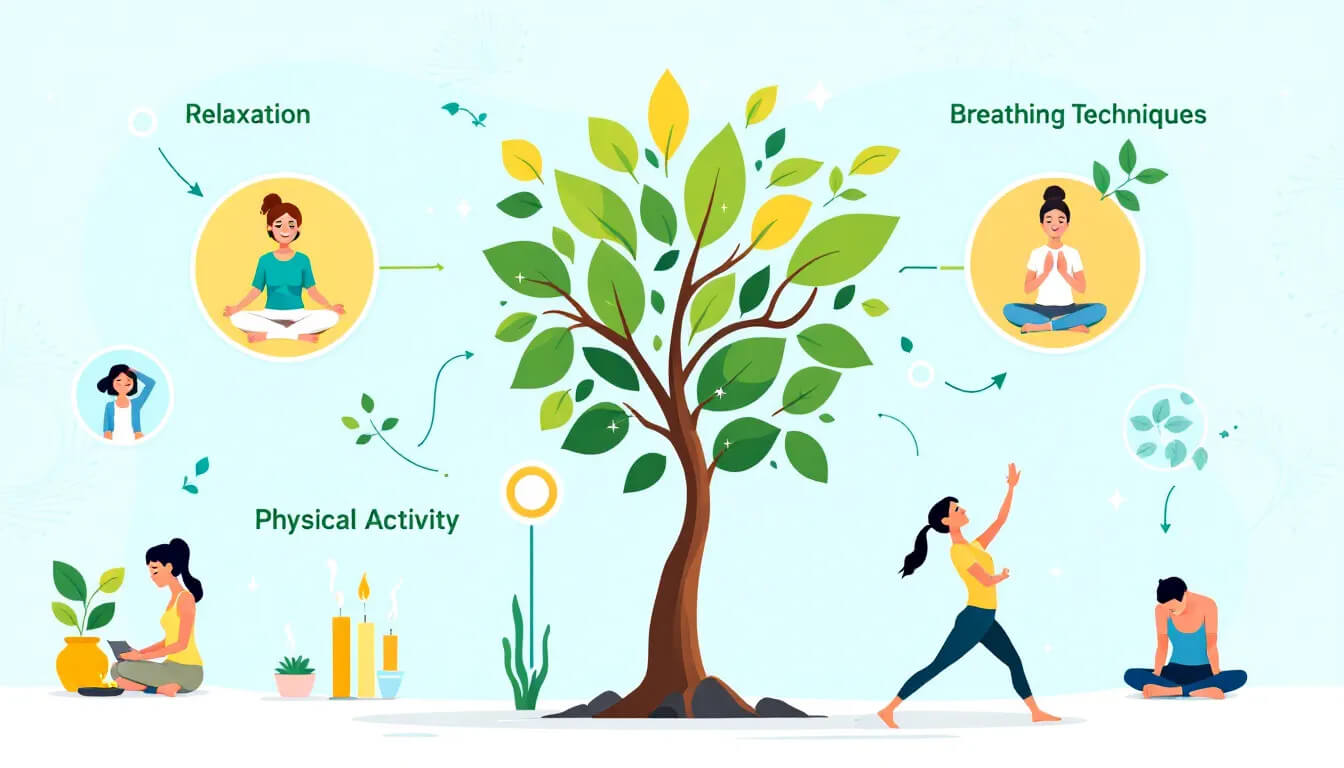
Managing stress effectively can significantly improve your oxygen levels and overall respiratory health. Breath control techniques, such as deliberate, slower breathing through the diaphragm, can help calm the nervous system and enhance relaxation. These techniques not only alleviate stress-related symptoms but also improve overall lung function.
Belly breathing is another effective technique that aids in better oxygen intake. Focusing on deep breaths that engage the diaphragm increases oxygen circulation in the body and reduces feelings of breathlessness, allowing the belly rise to enhance the overall breathing experience.
Mindfulness practices and engaging in social support groups can also play a crucial role in managing stress and improving respiratory health. Learning to connect with your mind and body can help you manage stress more effectively. This, in turn, positively affects your overall health.
The Importance of Mental Health in Respiratory Health
Mental health significantly affects how individuals manage their lung conditions and overall treatment adherence. Poor mental well-being can lead to decreased physical activity, which negatively impacts respiratory health. For those living with lung diseases, managing mental health is crucial for maintaining optimal lung function.
Living with a lung condition can trigger feelings of frustration and helplessness, contributing to anxiety and depression. These emotional challenges can further impact respiratory health, creating a cycle of difficulty that’s hard to break, especially for those with lung disease, other medical conditions, and an underlying condition.
Addressing mental health is, therefore, an integral part of improving respiratory health and overall well-being.
Home Oxygen Therapy as a Solution for Stress-Induced Low Oxygen Levels

Home oxygen therapy can be a lifesaver for those experiencing stress-induced low oxygen levels. This therapy is administered through devices like masks or portable canned oxygen, provided by reputable companies like REV/O2 Oxygen. Various devices, including supplemental oxygen concentrators and portable cylinders, cater to different patient needs.
Patients may require home oxygen therapy for varying durations, depending on their condition. Some older adults may need it only during activities, while others may require it continuously throughout the day and night.
It’s essential to follow safety measures, such as maintaining distance from open flames and ensuring proper ventilation, to use oxygen therapy safely at home.
Summary
In summary, stress has a profound impact on both mental and physical health, including the potential to lower oxygen levels in the body. By understanding the physiological responses to stress and how it affects breathing patterns, you can take proactive steps to manage stress and improve your respiratory health. Techniques like breathing exercises, mindfulness practices, and home oxygen therapy can make a significant difference in maintaining healthy oxygen levels.
As we navigate the complexities of our daily lives, it’s crucial to prioritize our mental and respiratory health. By managing stress effectively and monitoring oxygen levels, you can ensure that your body gets the oxygen it needs to function at its best. Take control of your health today and breathe easier tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does stress affect oxygen levels in the body?
Stress reduces oxygen levels in the body by causing rapid breathing and constricted airways. This physiological response diminishes the amount of oxygen that reaches the bloodstream.
What are the symptoms of low oxygen levels caused by stress?
Low oxygen levels caused by stress can lead to symptoms such as confusion, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, and a sensation of breathlessness. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention.
How can breathing exercises help manage stress-induced breathing difficulties?
Breathing exercises such as pursed lip breathing and belly breathing can effectively manage stress-induced breathing difficulties by controlling your breathing pace, enhancing oxygen intake, and fostering relaxation. Incorporating these techniques into your routine can lead to better stress management.
What is the role of home oxygen therapy in managing low oxygen levels?
Home oxygen therapy plays a crucial role in managing low oxygen levels by supplying supplemental oxygen through devices such as masks or portable units, thereby helping to maintain adequate oxygen saturation. This therapy is essential for individuals with conditions that impair oxygenation.
Why is mental health important for respiratory health?
Mental health is crucial for respiratory health because poor mental well-being can reduce physical activity, negatively affecting lung function. Addressing mental health is essential for overall respiratory wellness.












